CT Scan
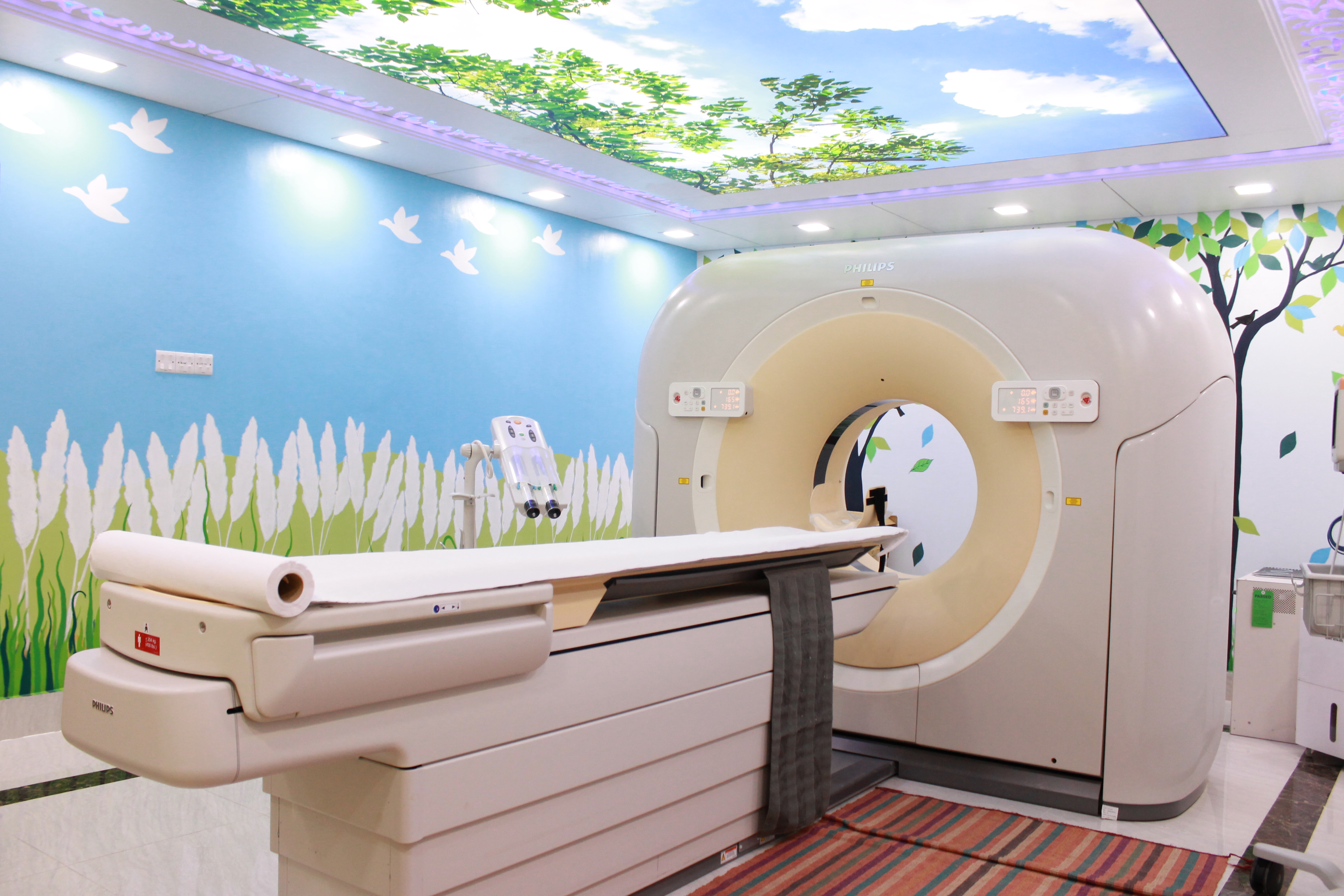
CT-scan (computed tomography) became available worldwide early 80’s. Since 2008, the practice of CT-scan has been started at Institute of Nuclear Medicine & Allied Sciences, Chattogram.
A CT Scan (also called "CAT" scan, which stands for Computerized Axial Tomography) is a diagnostic test which uses a series of X-rays to create cross sectional images or "slices".
A computer uses these slices to display two and three-dimensional images. CT images of internal organs, bone, soft tissue and blood vessels provide greater clarity and reveal more details than regular x-ray exams.
Other commonly performed CT exams include CT Angiography, Cardiac Calcium Scoring and Virtual Colonoscopy etc.
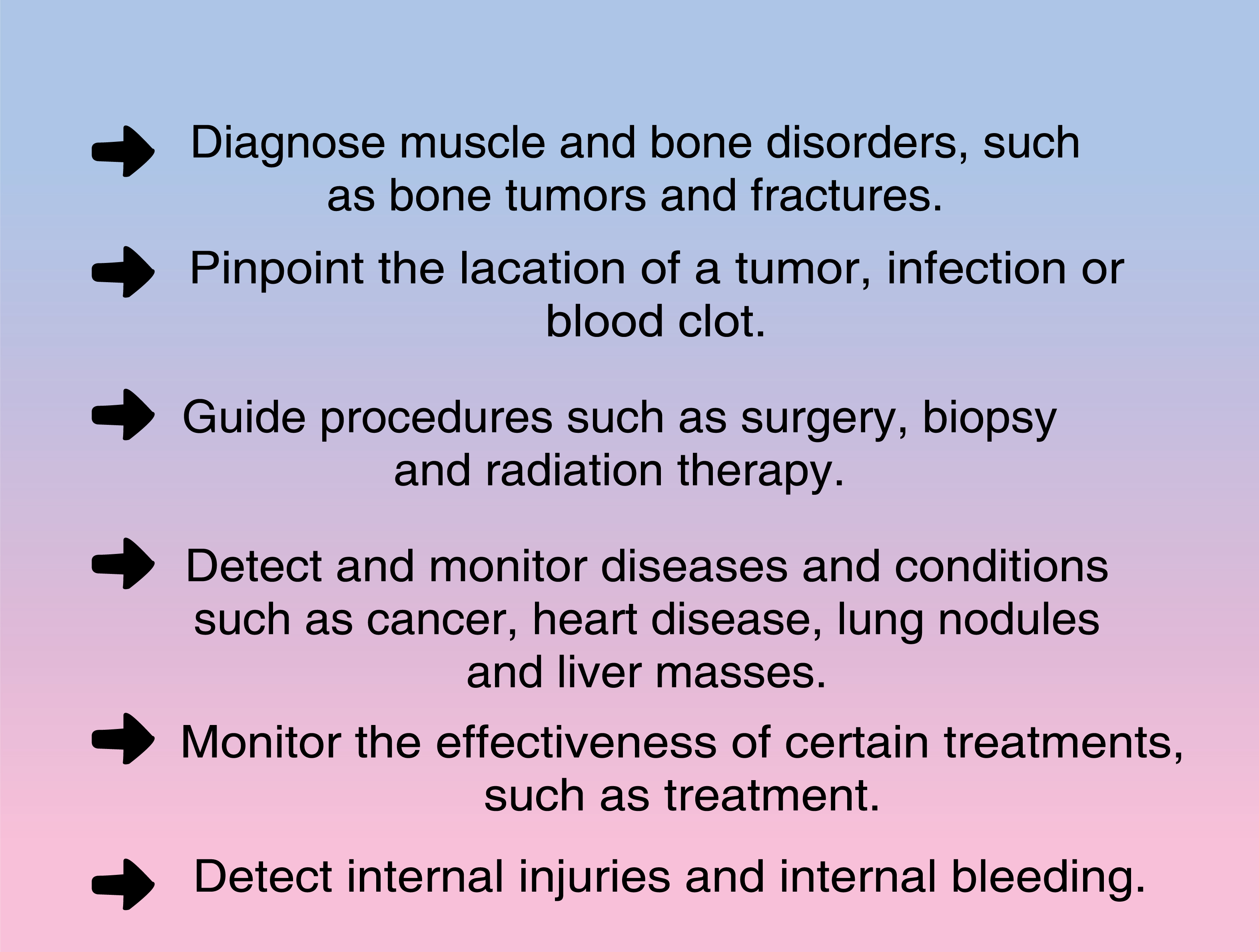
A CT scan has many uses, but it's particularly well-suited to quickly examine people who may have internal injuries from road-traffic accidents or other types of trauma. A CT scan can be used to visualize nearly all parts of the body and is used to diagnose disease or injury as well as to plan medical, surgical or radiation treatment.
Working Schedule
Working hour
Every Saturday to Thusday at 8.00am -2.30pm
Except Friday and all government holiday
Service Start Time
Every Saturday to Thusday at 7.30 AM
Except Friday and all government holiday
Alert
| Investigations | Rate | Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| SPECT Bone Scan | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT DTPA Cerebral imaging | 900 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT HMPAO Cerebral perfusion imaging (Tc-99m) | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Kidney Scan | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Liver Scan | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Lung perfusion | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Lung VQ Scan | 2500 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT MIBI parathyroid imaging (Tc-99m) | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Myocardial perfusion (rest) | 3500 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Myocardial perfusion (stress + rest) | 7000 | Get Appointment |
| Brain Scan | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| Brain tumor recurrence | 6000 | Get Appointment |
| Carcinoid tumor evaluation with octreotide | 11250 | Get Appointment |
| Liver Spleen Scan | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| Liver study for differentiation of benign Imalignant tumor with Tc-99m MAA | 1700 | Get Appointment |
| Lung VQ Scan | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| MIBG Scan | 11250 | Get Appointment |
| Oncological study MIBI, Thallium or Gallium | 9000 | Get Appointment |
| Other | 3500 | Get Appointment |
| Parathyroid | 4000 | Get Appointment |
| Salivary Scan | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| Whole body bone scan | 3000 | Get Appointment |
Your doctor may recommend a CT scan to help:
Radiation exposure
The low doses of radiation used in CT scans have not been shown to cause long-term harm, although at much higher doses, there may be a small increase in your potential risk of cancer. Doctors use the lowest dose of radiation possible to obtain the needed medical information. Also, newer, faster machines and techniques require less radiation than was previously used. Talk with your doctor about the benefits and risks of your CT scan.
Harm to the fetus (baby growing inside the uterus of the mother)
Tell your doctor if you're pregnant. Although the radiation from a CT scan is unlikely to injure your baby, your doctor may recommend another type of exam, such as ultrasound or MRI, to avoid exposing your baby to radiation. At the low doses of radiation used in CT imaging, no negative effects have been observed in humans.
Reactions to contrast material
In certain cases, your doctor may recommend that you receive a special dye called contrast material. This can be something that you are asked to drink before your CT scan, or something that is given through a vein in your arm or inserted into your rectum. Although rare, the contrast material can cause medical problems or allergic reactions.
Most reactions are mild and result in a rash or itchiness. In rare instances, an allergic reaction can be serious, even life-threatening.
Tell your doctor if you've ever had a reaction to contrast material.
Contrast material
A special dye called contrast material is needed for some CT scans to help highlight the areas of your body being examined. The contrast material blocks X-rays and appears white on images, which can help emphasize blood vessels, intestines or other structures. Contrast material might be given to you:
-
By mouth. If your esophagus or stomach is being scanned, you may need to swallow a liquid that contains contrast material. This drink may taste unpleasant.
-
By injection. Contrast agents can be injected through a vein in your aim to help your gallbladder, urinary tract, liver or blood vessels stand out on the images. You may experience a feeling of warmth during the injection or a metallic taste in your mouth.
-
By enema. A contrast material may be inserted in your rectum to help visualize your intestines. This procedure can make you feel bloated and uncomfortable.
Preparing your child for a scan
If your infant or toddler is having a CT scan, the doctor may recommend a sedative to keep your child calm and still. Movement blurs the images and may lead to inaccurate results. Ask your doctor how to prepare your child.
Required Time for CT scan procedure
You can have a CT scan done in a hospital or an outpatient facility. CT scans are painless and, with newer machines, take only a few minutes. The whole procedure typically takes about 30 minutes.
During the procedure
CT scanners are shaped like a large doughnut standing on its side. You lie on a narrow, motorized table that slides through the opening into a tunnel. Straps and pillows may be used to help you stay in position. During a head scan, the table may be fitted with a special cradle that holds your head still. While the table moves you into the scanner, detectors and the X-ray tube rotate around you. Each rotation yields several images of thin slices of your body. You may hear buzzing and whirring noises. A technologist in a separate room can see and hear you. You will be able to communicate with the technologist via intercom. The technologist may ask you to hold your breath at certain points to avoid blurring the images. CT images are stored as electronic data files and are usually reviewed on a computer screen.
After the procedure
After the exam you can return to your normal routine. If you were given contrast material, you may receive special instructions. In some cases, you may be asked to wait for a short time before leaving to ensure that you feel well after the exam. After the scan, you'll likely be told to drink lots of fluids to help your kidneys remove the contrast material from your body.
