Gamma Camera
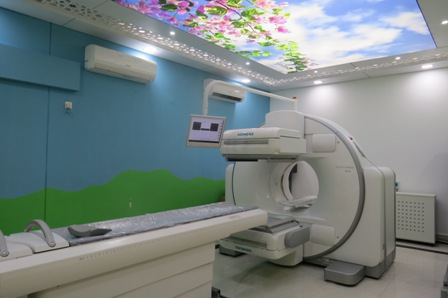
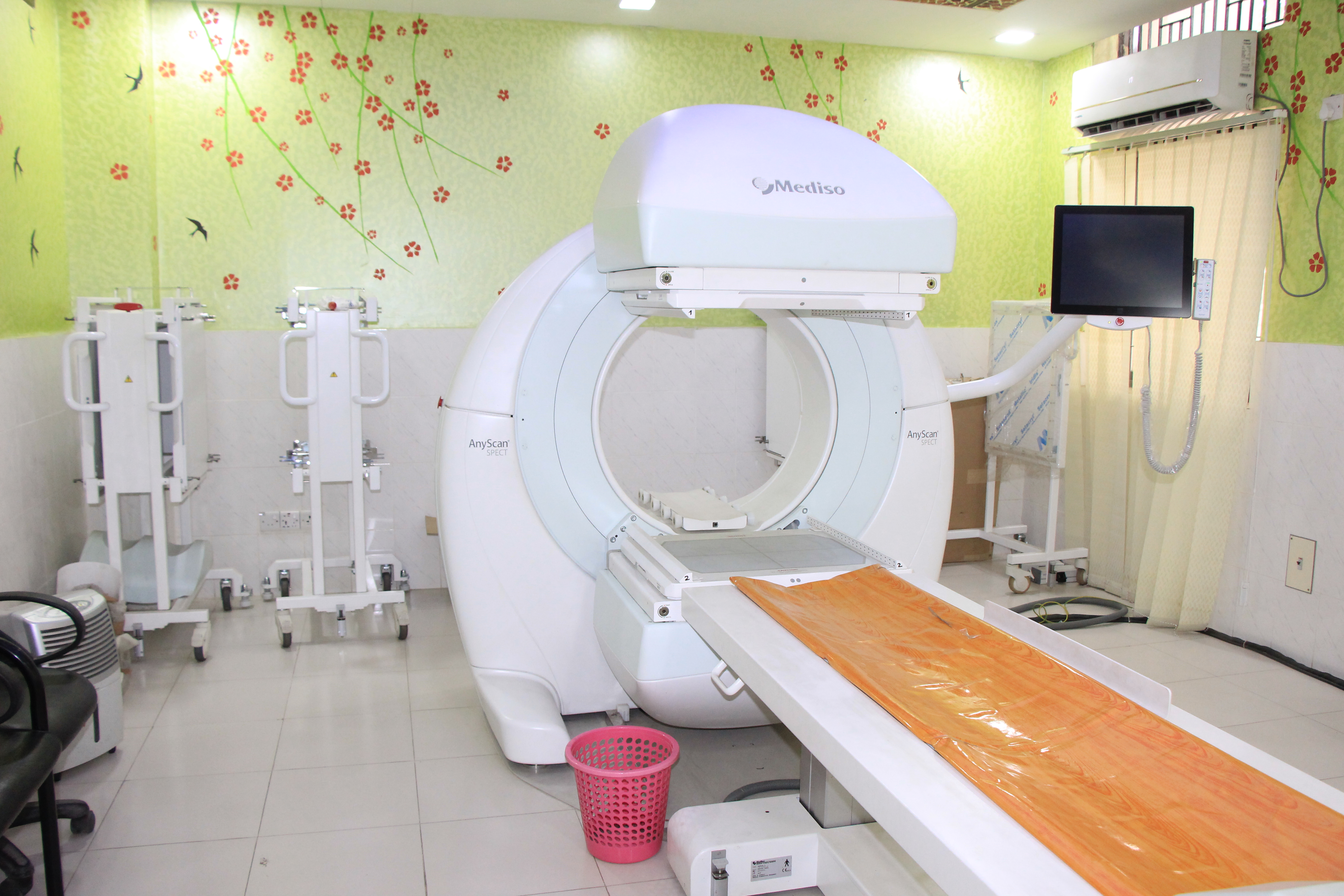
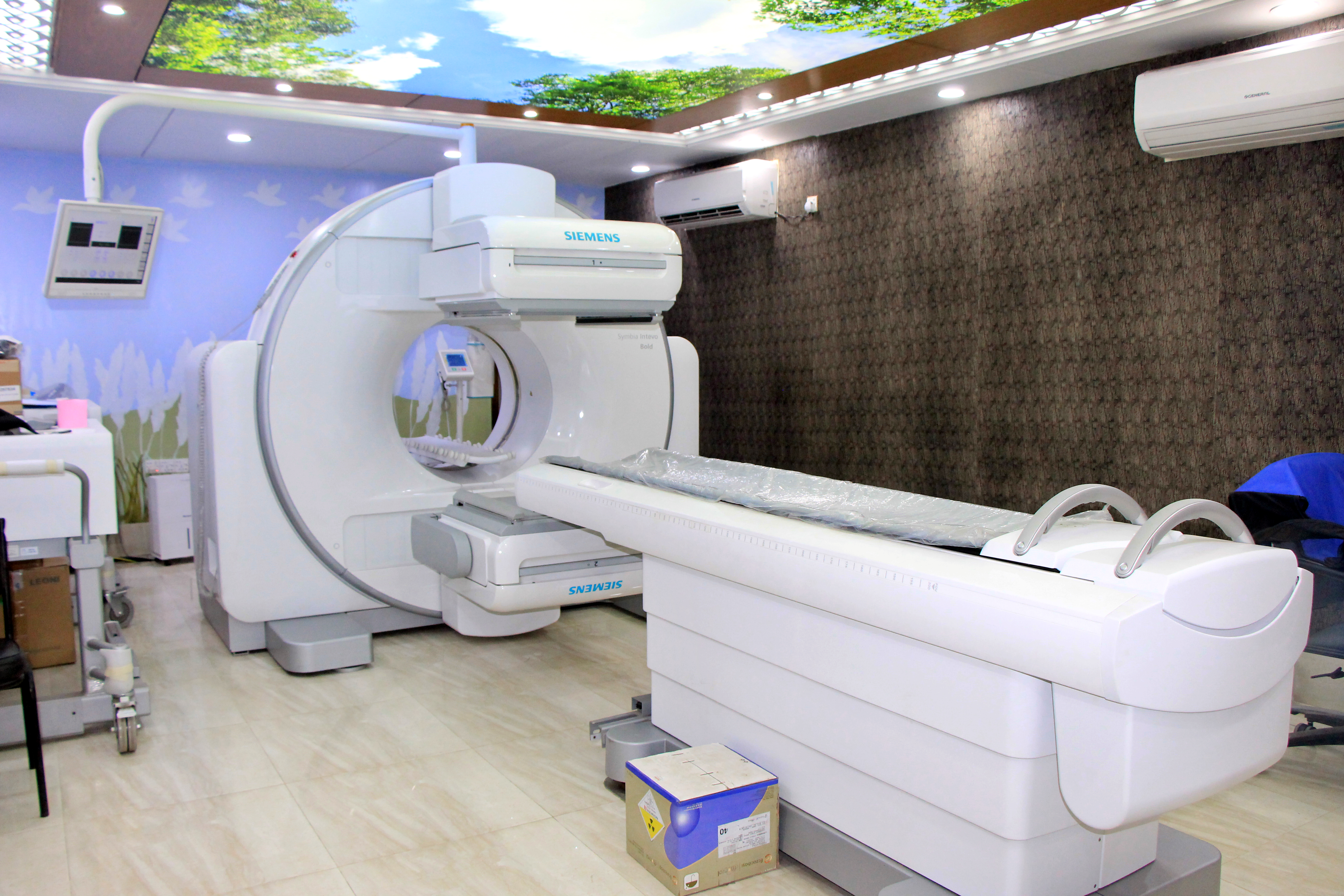
Gamma Camera: The special camera and imaging techniques used in nuclear medicine include the Gamma camera and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). The Gamma camera, also called a scintillation camera, detects radioactive energy that is emitted from the patient's body and converts it into an image. It simultaneously detects radiation from the entire field of view and enables the acquisition of dynamic as well as static images of the area of interest in the human body.
Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose, evaluate or treat a variety of diseases. These include many types of cancers, heart disease, gastrointestinal, endocrine or neurological disorders and other abnormalities. Because nuclear medicine exams can pinpoint molecular activity, they have the potential to identify disease in its earliest stages. They can also show whether a patient is responding to treatment. Nuclear medicine imaging procedures are non-invasive. With the exception of intravenous injections, they are usually painless.
Depending on the type of exam, the radiotracer is injected, swallowed or inhaled as a gas. It eventually accumulates in the area of the body under examination. A special camera or imaging device detects radioactive emissions from the radiotracer. The camera or device produces pictures and provides molecular information.
Many centers superimpose nuclear medicine images with computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to produce special views. This is known as image fusion or co-registration. These views allow the doctor to correlate and interpret information from two different exams on one image this leads to more precise information and accurate diagnoses. Single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (SPECT/CT) and positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) units can perform both exams at the same time.
Working Schedule
Working hour
Every Saturday to Thusday at 8.00am -2.30pm
Except Friday and all government holiday
Service Start Time
Every Saturday to Thusday at 7.30 AM
Except Friday and all government holiday
The department started the service at 7.30 am
(The certain patient will be appointed according to the availability of Radio Isotopes and Kit)
Alert
| Investigations | Rate | Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac first pass | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Cardiac MUGA | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| DMSA-Renal Scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Brain Scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Captopril Renogram (Tc-99m) | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Renogram and Serum sample GFR (Tc-99m) | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Renogram and Split Renal Function (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Renogram with camera GFR (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| DTPA-Scan for Soft tissue tumor (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| Gallium tumor/infection evaluation | 3500 | Get Appointment |
| Hepatobiliary scan (Tc-99m) | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| Hysterosalphingo Scintigraphy (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| I-131 Thyroid Scan | 500 | Get Appointment |
| Liver flow scan (Tc-99m) | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| Liver scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Liver Spleen Scan (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| Lung perfusion (planner) | 1200 | Get Appointment |
| Lung VQ Scan (planner) | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| Lymphoscintigraphy for lymphatic drainage evaluation (Tc-99m) | 1500 | Get Appointment |
| Lymphoscintigraphy for sentinel LN (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Meckels Diverticulums Scan (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| MIBI Parathyroid Imaging Planner (Tc-99m) | 1700 | Get Appointment |
| Probe Renogram | 600 | Get Appointment |
| RBC-Scan for Gastrointestinal bleeding (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| RBC-Scan for Hemangioma (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| Salivary Scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Serum Sample GFR | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Shunt patency study | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| Single spot Bone scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Bone Scan (Planner) | 2500 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT HMPAO Cerebral prefusion Imaging (Tc-99m) (Planner) | 2250 | Get Appointment |
| SPECT Myocardial Perfusion (Planner) | 2250 | Get Appointment |
| Tc 99m Brain Scan | 600 | Get Appointment |
| Testicular Scan (Tc-99m) | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Three phase Bone scan (Tc-99m) | 3000 | Get Appointment |
| Thyroid Scan (Tc-99m) | 500 | Get Appointment |
| Thyroid uptake study | 400 | Get Appointment |
| Vesicoureteric reflux study | 800 | Get Appointment |
| Whole body Bone scan (Tc-99m) | 1000 | Get Appointment |
| Whole body Iodine Thyroid scan with I-131 | 1200 | Get Appointment |
Common Clinical Applications
- Bone scan:- to assess metabolic activity of the bones Commonly Used for oncology staging, arthritis, fractures.
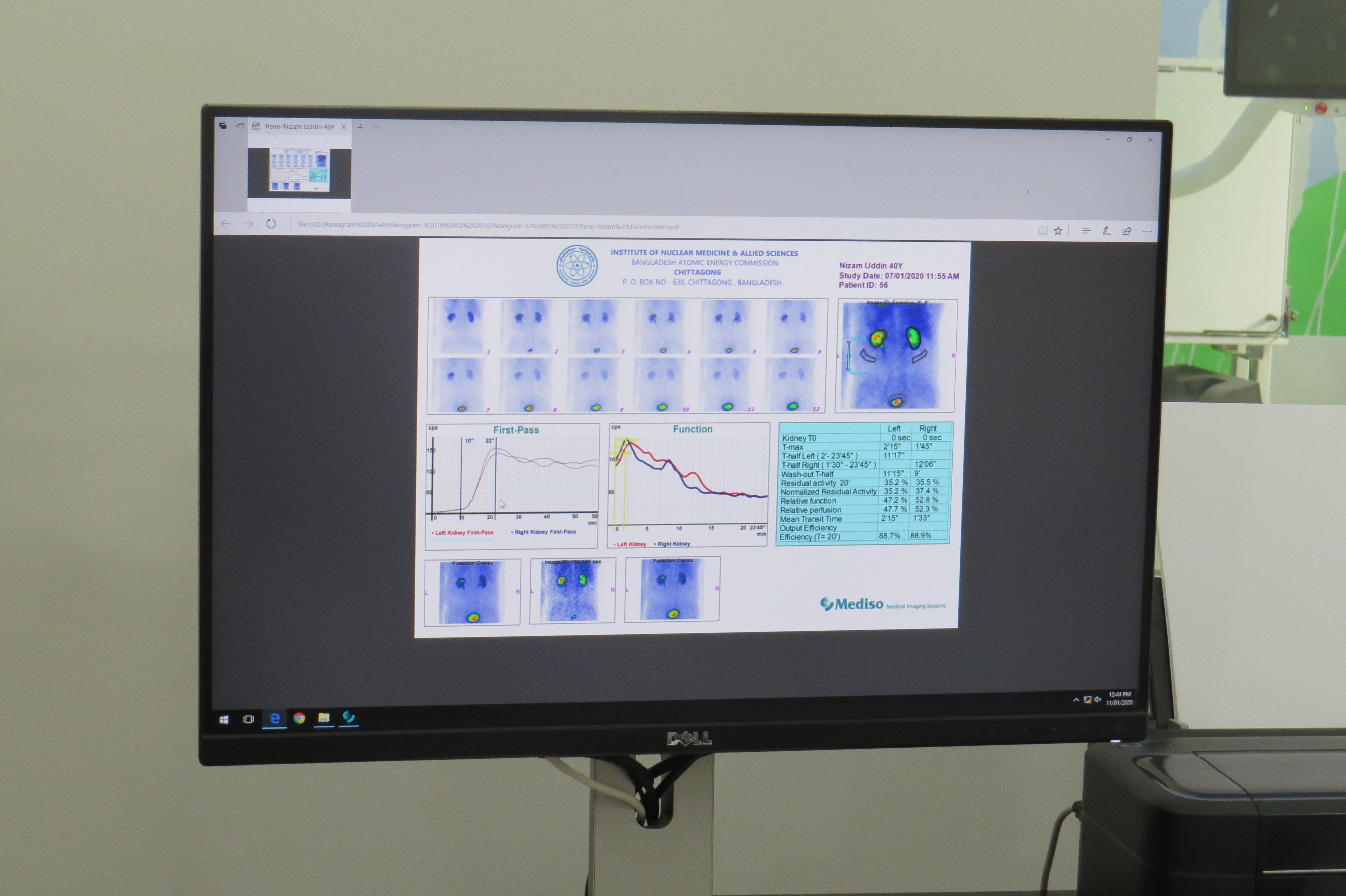
- Renal scan & Renogram:- to determine the perfusion and drainage of the kidneys and allow for calculation of differential function.
- Thyroid scan:- to assess the appearance and function of the thyroid gland.
- Myocardial Perfusion scan:- to compare the blood flow to the myocardial at exercise and rest allowing for differentiation of Ischaemia and infarction.
- Lung scan (VQ):- to allow for comparison of ventilation and perfusion of the lungs to diagnose pulmonary embolism.
Safety
- Pregnancy status must be established prior to procedure. Performance of a Nuclear Medicine study on a pregnant woman must be clinically justified, with the administered dose minimized.
- Breast feeding women may need to cease breast feeding dependent on the procedure being performed. This is due to excretion of the radiotracer in the breast milk.
- Children are particularly radiosensitive; therefore non radiation imaging modalities such as ultrasound and MRI should be utilized if possible. When performing Nuclear Medicine studies on pediatric patients the radioactive dose is scaled according to the patient's weight.
- To aid excretion of the tracer via the urinary tract, the patient may be instructed to remain well hydrated and urinate frequently to reduce radiation dose.
- Patients undergoing therapy procedures will be given specific
instructions regarding radiation safety.
Preparation (Bone scan & Renogram) :
Bone Scan PDF/Print
Renogram PDF/Print